Describe the Arrangement of the Layers of Smooth Muscle
Although they do not have striations and sarcomeres smooth muscle. Construction of these muscles helps mix and break the contents into a suspension of nutrients called chyme and propels it into the.

Epithelial Tissue Is Composed Of Tightly Connected Cells Arranged In One Or More Layers Epithelia Tissue Biology Science Biology Human Anatomy And Physiology
Note again the spindle-shaped cells and centrally located nucleus in each cell.

. Next to that you see a lighter region of connective tissue the submucosa you looked at to see loose connective tissue and fibroblasts then a darker pink region which is made up of the two layers of smooth muscle you want to look at. Describe the arrangement of the layers of smooth muscle in the seminal gland 24. Inside each skeletal muscle muscle fibers are organized into bundles called fascicles surrounded by a middle layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.
What is the function of the stereocilia exhibited by the epithelial cells of the mucosa of the epididymis. Within the muscularis externa the circular muscle layer prevents food from traveling backward while the longitudinal layer shortens the tract. A thin interstitial space 5.
The purple layer is largely the epithelium and the lamina propria filled with plasma cell and lymphocytes. Desc ribe the arrangement of the layers of smooth muscle in the seminal gland. Describe the epithelium found in the uterine tube.
These thin filaments are anchored by dense bodies. Non-striated muscle is synonymous with smooth muscle and has an irregular arrangement of actin and myosin. They range from about 30 to 200 μm thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and they produce their own connective tissue endomysium.
What is the function of the stereocilia exhibited by the epithelial cells of the mucosa of the epididymis. More gap junctions between adjacent muscle fibers are found in the circular layer than in the longitudinal muscle layer. For the vasculature smooth muscle is arranged in two individual layersan inner circular layer of smooth muscle and an outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle.
There is also a network of supporting collagenous tissues between the fibers and the fasciculi. The smooth muscle in the intestine is arranged into two layers. Describe the epithelium found in the uterine tube.
Describe the epithelium found in the uterine tube. The basement membrane of the alveolar epithelium 4. The alveolar epithelium composed of simple squamous epithelium 3.
Describe the arrangement of the layers of smooth muscle in the seminal gland 24. Inside each skeletal muscle muscle fibers are organized into individual bundles each called a fascicle by a middle layer of. Inside each skeletal muscle muscle fibers are organized into individual bundles each called a fascicle by a middle layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.
Muscle fibers are covered by the endomysium. Understand the locations and rolesof intercellular junctions in muscle. These fasciculi are the functional contractile units.
This fascicular organization is. This fascicular organization is common in muscles of the limbs. For arteries the circular layer is much thicker than the longitudinal layer owing to the fact that the artery must contract to increase vascular resistance against arterial pressure.
Desc ribe the arrangement of the layers of smooth muscle in the seminal gland. Bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles are covered by the perimysium. Intracellular release from internal stores is more important for excitation-contraction coupling in the muscle fibers of the circular.
Bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles are covered by the perimysium. A thin layer of fluid lining the alveolus 2. Figure 1021 The Three Connective Tissue Layers.
You can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular systemThis type of involuntary non-striated muscle is also found in the tracts of the urinary. Describe the epithelium found in the uterine tube. The three layers of smooth muscle consist of the outer longitudinal the middle circular and the inner oblique muscles.
The basement membrane of the capillary endothelium 6. Although smooth muscle cells do not have striations smooth muscle fibers do have actin and myosin contractile proteins which interact to generate tension. Although they do not have striations and sarcomeres smooth muscle fibers do have actin and myosin contractile proteins and thick and thin filaments.
It allows the nervous system to trigger a specific movement of a muscle by activating a subset of muscle fibers within a bundle or. All muscle tissue is derived from mesoderm the middle embryonic germ cell layer. Understand the arrangement and roles of transverse tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum mitochondria and contractile filaments in the process of contraction 6.
It consists of several layers. These fibers are not arranged in orderly sarcomeres hence no striations but instead are anchored to dense bodies which are scattered throughout the cytoplasm and anchored to the sarcolemma. Muscle fibers are covered by the endomysium.
Calcium influx from outside the muscle cells is important for excitation-contraction coupling in longitudinal muscle fibers. The layers are not truly longitudinal or circular rather the layers of muscle are helical with different pitches. Composed of two layers of smooth muscle with fibers in one layer having perpendicular.
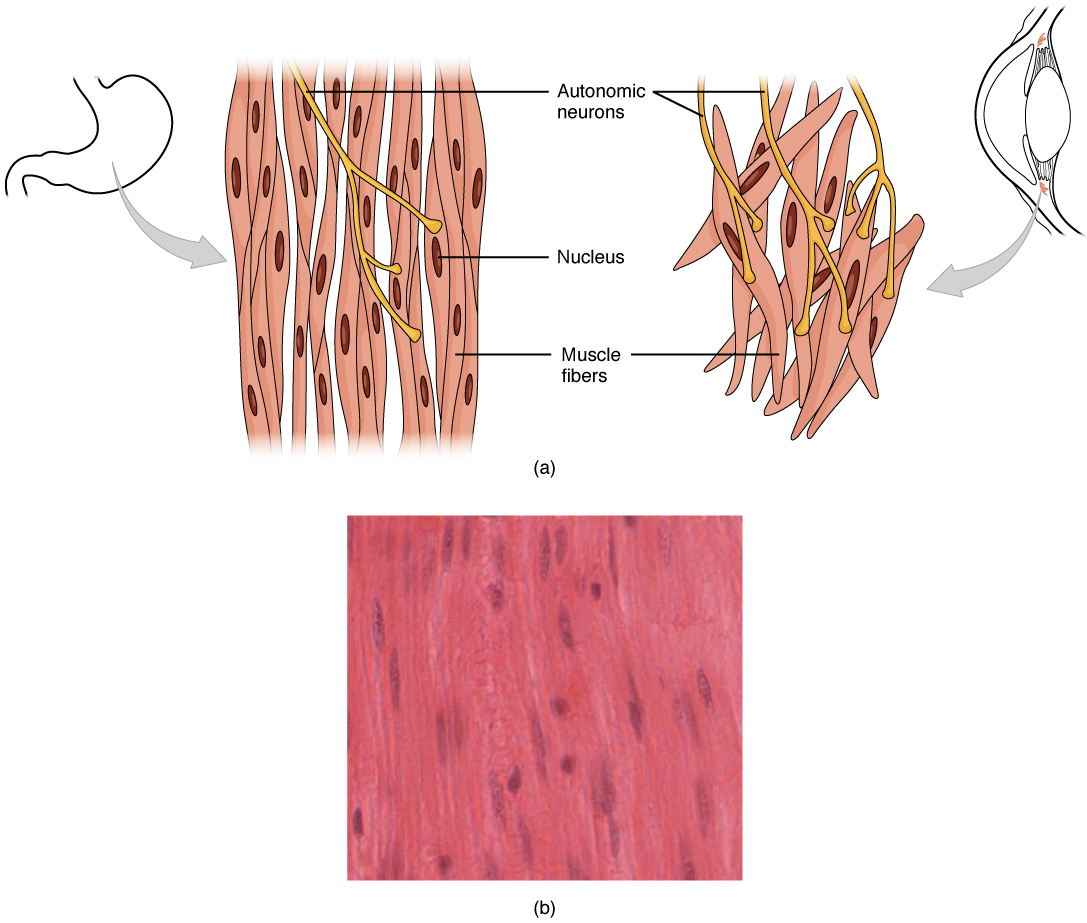
An inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. Smooth muscle fibers are spindle-shaped wide in the middle and tapered at both ends somewhat like a football and have a single nucleus. The muscularis mucosa is made up of smooth muscle and is most prominent in the stomach.
Describe the arrangement of the layers of smooth muscle in the seminal gland. Smooth muscle Textus muscularis levis Smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines uterus and stomach. A dense body is analogous to the Z-discs of skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers and is fastened to the sarcolemma.
Smooth muscle fibers are bound together in irregular branching fasciculi that vary in arrangement from organ to organ.
Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Describe the Arrangement of the Layers of Smooth Muscle"
Posting Komentar